Understanding SADI-S Gastrectomy
SADI-S gastrectomy (single anastomosis duodenoileal bypass with sleeve gastrectomy) is a relatively new bariatric surgical procedure combining elements of sleeve gastrectomy and duodenal switch. It aims to promote significant weight loss by both restricting food intake (via stomach reduction) and altering nutrient absorption (via intestinal rerouting). Unlike simpler procedures like the sleeve gastrectomy, SADI-S offers a more aggressive approach to weight management.
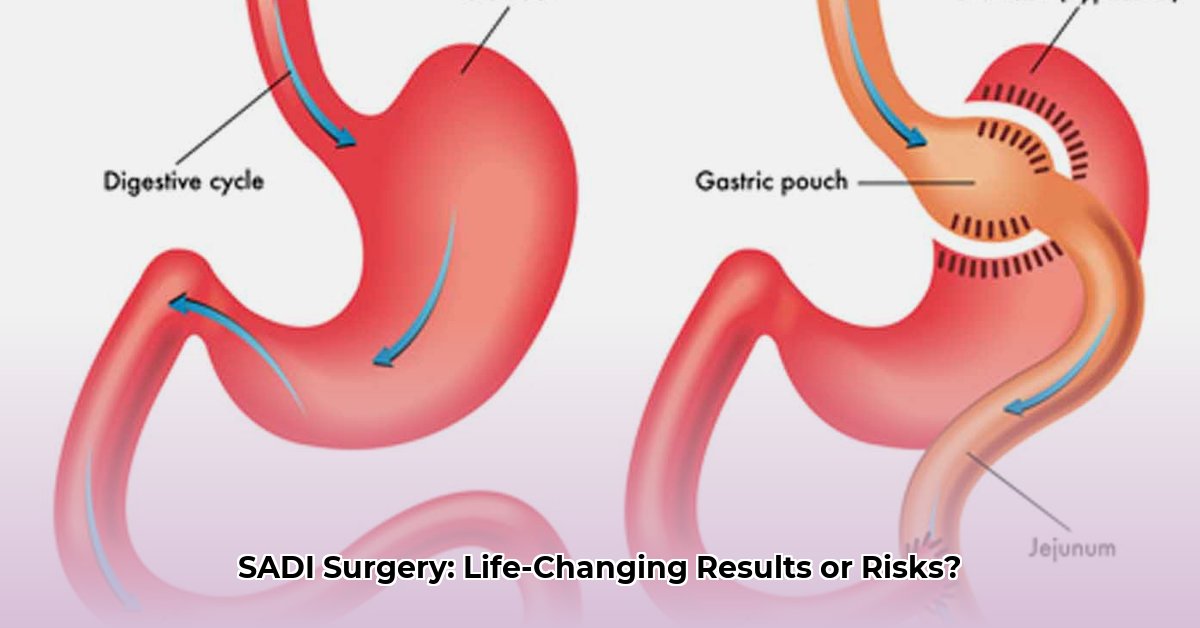
How SADI-S Works
The SADI-S procedure involves a sleeve gastrectomy, reducing the stomach's size to limit food intake. Simultaneously, a portion of the small intestine is bypassed, reducing nutrient absorption. This dual-action approach aims for substantial and sustained weight loss, but carries a higher risk profile than simpler procedures.
Efficacy of SADI-S: Short-Term and Long-Term Outcomes
Early studies suggest significant short-term weight loss with SADI-S, often exceeding expectations. However, long-term data remains limited. While many patients maintain significant weight loss, the potential for weight regain necessitates continuous monitoring and lifestyle adjustments. Further research is crucial to solidify long-term efficacy claims.
Risks and Complications of SADI-S
SADI-S, like all surgeries, carries risks. These include:
- Infection: A moderate likelihood of high severity. Mitigation involves sterile surgical techniques, prophylactic antibiotics, and vigilant wound care.
- Anastomotic Leak: Moderate likelihood, high severity. Meticulous surgical technique, careful post-operative monitoring, and immediate intervention are vital.
- Bile Reflux: Moderate likelihood, moderate severity. Specialized surgical approaches, dietary modifications, and medication may be employed.
- Intestinal Perforation: Low likelihood, very high severity. Expert surgical technique and immediate post-operative attention are critical for prompt management.
- Bowel Obstruction: Low likelihood, high severity. Prophylactic measures during surgery and vigilant post-operative care are necessary.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Moderate likelihood, moderate severity. Regular blood tests, tailored vitamin and mineral supplementation, and nutritional counseling are crucial for management.
These risks highlight the importance of careful patient selection and rigorous post-operative care.
Patient Selection for SADI-S
Ideal candidates for SADI-S typically have a high body mass index (BMI) and poorly controlled type 2 diabetes. However, individual circumstances significantly influence suitability. A thorough pre-operative assessment—including a review of medical history, comorbidities, and psychological factors—is mandatory. The decision to proceed should be jointly reached by the patient and their surgical team after a comprehensive evaluation.
Recovery and Post-Operative Care
Recovery from SADI-S involves a period of adjustment. Patients must strictly adhere to post-operative dietary guidelines, gradually introducing foods to allow for proper adaptation. Regular follow-up appointments are essential for monitoring progress, managing potential complications, and addressing nutritional deficiencies. Long-term commitment to dietary and lifestyle changes is crucial for sustained weight loss and preventing complications.
Comparison to Other Bariatric Procedures
SADI-S offers significant weight loss, comparable to more complex procedures like the duodenal switch. However, it carries a higher risk profile compared to other revisional procedures, such as one-anastomosis gastric bypass (OAGB). The choice of procedure depends on individual factors and should be determined after a thorough discussion with a qualified bariatric surgeon.
Conclusion: A Balanced Perspective on SADI-S
SADI-S demonstrates promising short-term weight loss results. However, the limited long-term data necessitates further research to fully understand its long-term effects and compare it definitively against other bariatric procedures. Careful patient selection, meticulous surgical technique, and diligent post-operative management are paramount to minimizing risks and maximizing positive outcomes. This information serves as an overview and should not substitute for individual consultations with healthcare professionals.